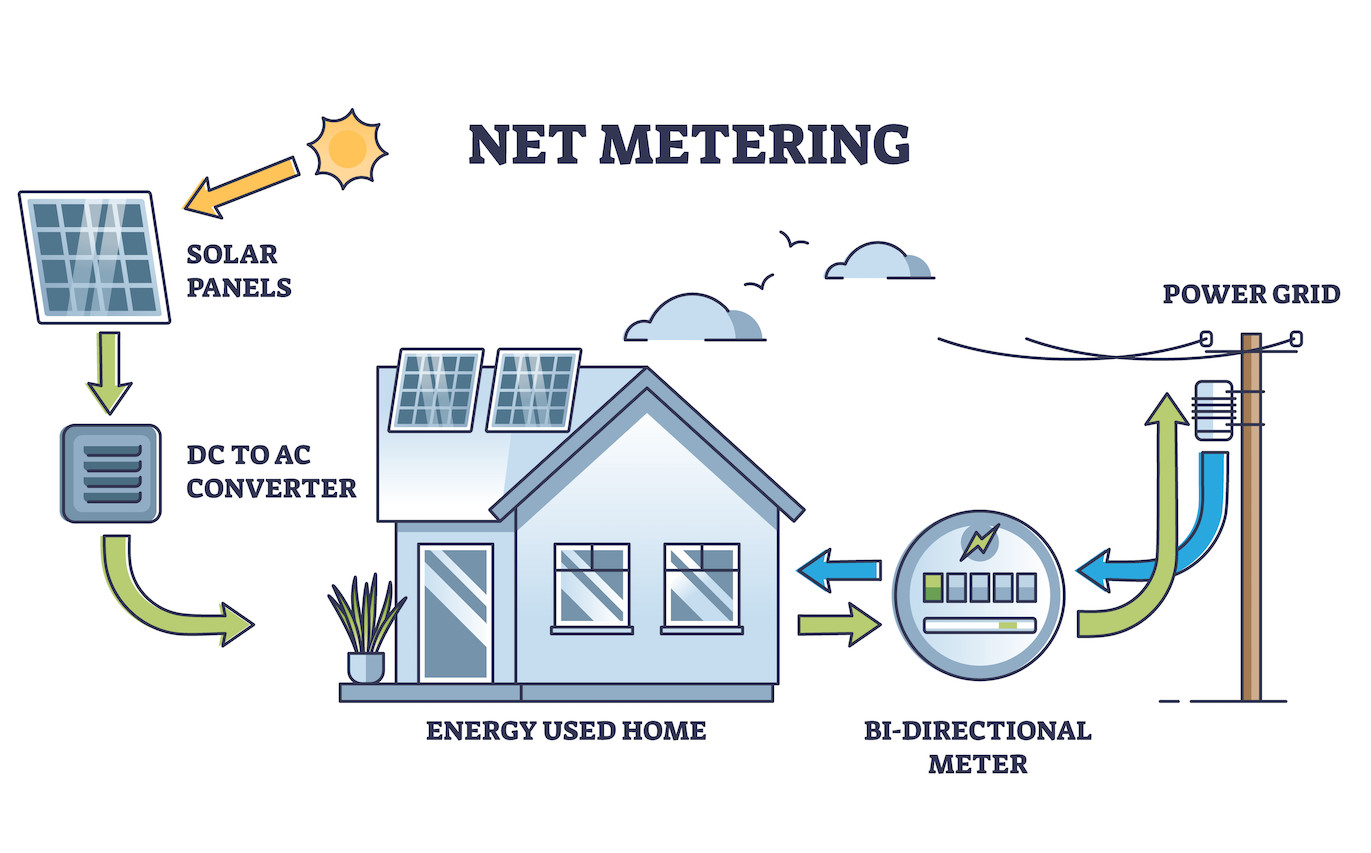
NEM 2.0 and NEM 3.0 are like day and night. While the former net metering strategy generously rewards all homeowners for solar installations, the other makes doing the right thing for the environment far less profitable. Both strategies allow homeowners with solar to sell excess energy back to the grid, but NEM 3.0 cuts the resulting compensation by up to 75%.
In this article, we’ll outline the biggest differences of NEM 2.0 vs. NEM 3.0 to help you understand the net metering rules in California.
Key Differences of NEM 2.0 vs. NEM 3.0
Effective April 15, 2023, NEM 3.0 decreases sell-back rates for all new solar installations. It also gradually grandfathers older systems into the far less munificent reward system over the next 20 years.
NEM 3.0 made several notable changes to California’s net metering policy and the benefits it brought to homeowners. Some of the most important differences between NEM 2.0 vs. NEM 3.0 include:
- The value of export rates
- Instantaneous netting
- Removal of the grid participation charge
Keep reading to learn more about how these changes will affect you and your decision to go solar.
1. The Value of Export Rates
NEM 3.0 will reduce the value of net metering credits and extend the solar payback period for customers who generate electricity with their renewable energy sources. This means it will take longer for homeowners to receive a positive return on their investment in solar energy.
With NEM 2.0, customers received a full retail rate for any excess electricity they exported to the grid. This allowed them to pay off their solar system more quickly.
Under the new NEM 3.0 rules, export rates are being reduced by about 75%. This means you will receive less money for the energy you sell back to your utility company, making it harder to pay off your system.
2. Instantaneous Netting
Under NEM 2.0, electricity rates were calculated every hour based on a user’s net generation and usage during that hour. This is considered to be more favorable toward solar customers since peak hours of consumption (Such as night) can be offset by higher levels of production during the day.
NEM 3.0 will enact instantaneous netting (or rapid cycling), allowing meters to communicate in real-time instead of hourly. Instantaneous net metering will benefit customers less and be more complex to calculate.
3. Grid Participation Charge
NEM 3.0 will introduce a “Mandatory Grid Participation Charge,” which requires all participants to pay a fee for using the network’s resources and services. Solar customers can expect to pay an extra $8 charge per kilowatt (kW) of solar power capacity. This means the average homeowner will have to pay an additional $48 per month, further reducing the amount of savings received from solar energy.
Effects of NEM 3.0
Under NEM 2.0, California residents were often able to recoup their investments in solar energy within just 5-6 years. The high purchasing rates for excess energy under the NEM 2.0 scheme paired with a lower reliance on the grid meant that solar installations rapidly paid for themselves. Unfortunately, under NEM 3.0, the average payback period for new solar installations has increased to 14-15 years, about triple the payback period of NEM 2.0. While net metering schemes are intended to incentivize solar installation, NEM 3.0 does quite the opposite.
Grid Participation Fees
Under NEM 3.0, all California utility companies will charge mandatory grid participation fees. For instance, while having solar once meant paying just $10 per month as a flat rate, an interconnection fee under NEM 2.0, solar users will now pay $8 per kW of solar capacity. With 6 kW being the capacity of the average system, most homeowners with solar can expect to pay $48 each month for mere grid participation.
Lower Lifetime Savings
NEM 3.0 has also significantly decreased the lifetime savings of new solar installations. While homeowners could enjoy up to $116k in savings throughout the lifespans of their equipment, the new NEM 3.0 buy-back scheme reduces this to just $73k, and this is in best-case scenarios only.
Lock-In Periods
Another major drawback of NEM 3.0 is that it requires homeowners to lock into export rates for nine years. Only after nine years have passed will utility companies review and reset these rates, and then, only once every two years.
Invest in Solar Batteries
Now that NEM 3.0 has greatly diminished the financial incentives of having a standard, rooftop solar system, homeowners can still optimize their savings with solar batteries, like the Tesla Powerwall 3. Solar batteries store unused energy for future use so that homeowners aren’t selling it to utility companies at substandard rates. Other benefits of solar batteries include:
- Help You Pay Less During High Demand Times: Since solar batteries store energy for later use, they allow you to have a supply during peak energy times like at night or when it’s cloudy.
- Sell Energy Back: Get the most bang for your buck by selling energy back to the grid during nighttime hours when export rates are at their highest.
- Become Energy Independent: Rely less on the grid with your own supply of energy coming right from your solar panels.
Get Energy Peace of Mind With Solar Optimum’s Battery Solutions
With solar batteries, solar installation remains the most cost-effective and eco-conscious way to power your home despite the unfortunate changes that NEM 3.0 has wrought. Solar Optimum can help you use the latest solar technologies to cut your overhead costs, carbon footprint and grid dependency. Contact us to learn how you can future-proof your home solar system.